LIGHT, CBSE CLASS X, PHYSICS NOTES PART I
CBSE CLASS 10, LIGHT, PHYSICS NOTES - (PART I)
LIGHT
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2025-26
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Notes
TOPICS
1. Introduction.
2. Properties of light.
3. Reflection.
-Laws of reflection.
-Virtual and real image.
4. Image formed by a plane mirror.
-Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
-Lateral inversion and its application.
5. Spherical mirrors.
-Properties of a concave mirror.
-Properties of a convex mirror.
-A common term for spherical mirrors.
6. Rules for making ray diagrams by spherical mirrors.
7. Ray diagrams for images formed by a concave mirror.
-When an object is at infinity.
-When an object is beyond C.
-When an object is at C.
-When an object is placed between F and C.
-When an object is placed at F.
-When an object is between P and F.
8. Uses of a concave mirror.
9. Ray diagram of the image formed by the convex mirror.
-When an object is placed at infinity.
-When an object is placed between the pole and infinity.
10. Uses of a convex mirror.
11. Sign convention for reflection by a spherical mirror.
12. Mirror formulas.
-Magnification of a spherical mirror.
INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT – REFLECTION & REFRACTION
In Class 10 Science Chapter 10, Light, the phenomena of reflection and refraction of light, using the straight-line propagation of light, are taught to students. Furthermore, optical phenomena in nature are examined. The reflection of light by spherical mirrors is discussed in the chapter, allowing for an examination of their applications in real-life situations.
LIGHT: DEFINITION
Light is a form of energy that enables us to see things. Light starts from a source and bounces off objects, which are perceived by our eyes, and our brain processes this signal, which eventually enables us to see. Some common phenomena associated with light are image formation by mirrors, the twinkling of stars, the beautiful colours of a rainbow, the bending of light by a medium, and so on. Maxwell predicted that magnetic and electric fields travel in the form of waves, and these waves move at the speed of light. This led Maxwell to predict that light itself was carried by electromagnetic waves, which means that light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
Light is the form of
energy that provides a sensation of vision.
NATURE OF LIGHT
Light behaves as
a:
a.
ray, e.g., reflection
b.
wave, e.g., interference and diffraction
c.
particle, e.g., photoelectric effect
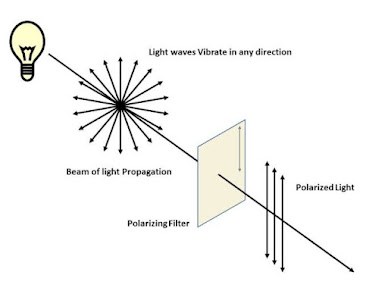
According to the concept of wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics, light exhibits both particle and wave nature, depending upon the circumstances. A phenomenon like diffraction, polarisation, and interference could be explained by considering light as a wave. A phenomenon like the photoelectric effect is explained by assuming that light consists of particles called photons.
Image
formation by mirrors includes the twinkling of stars, the beautiful color of a rainbow, the bending of light by a medium, and so on. And it is light that makes us see
our image in a looking mirror. We detect with our eyes.
We also need a source of light to make objects visible. It is only when light coming from an object enters our eyes that we can see that object. This light may have been emitted by the object itself, or it may have been reflected by the object. PROPERTIES OF LIGHT
Light enables us to see objects from which it comes or from which it is reflected. For example, the sun gives out light. We can see because the light coming from the sun enters our eyes. The object that emits its own light is known as a luminous object.
a.
Electromagnetic wave, so it does not require any medium to travel.
b. Light tends to travel in a straight line.
c. Light has a dual nature, i.e., wave as well as particle.
d. Light casts a shadow. e. The speed of light is maximum in a vacuum. Its value is 3 × 108 ms-1.
When light falls on a surface, the following may happen:
(i) Reflection
(ii) Refraction
(iii) Absorption
The objects, like a flower, a chair, or a table, do not have the light of their own light, but even then
we are able to see them. Though objects like a flower, a chair or a
table, bricks, etc do not emit light, we can see them by the light which they
reflect or scatter by taking it from a luminous object.
Those objects that do not emit light by their own but only reflect or scatter the light that falls on them are called non-luminous objects.
A flower, chair, table, book, trees, other planets, human being fan, bad, mirror, diamond, wall, floor, and Road, etc., are non-luminous objects. In fact, most of the objects around us are non-luminous.
We can see the non-luminous object because it receives light from the luminous object and reflects the light into our eyes. So we can say that light is a form of energy that causes a sensation of sight.
Nature of light
There are two theories about the nature of light: the wave theory of light and the particle theory of light. Some of the phenomena of light can be explained only if the light is considered to be made up of waves. Whereas others can be explained only if the light is made up of particles.
According to the Wave theory, light
consists of electromagnetic waves which do not require a material medium, for
example, solid, liquid, or gas for their propagation. The wavelength of visible light waves
is very small. The speed of a light wave is very high; it is about 3 × 108
meters per second in a vacuum.
According
to particle theory, light is composed of particles that travel in a straight line
at very high Speed. The elementary particle that defines light is a Photon.
For example,
1. Diffraction bending of light.
2. Interference
3. Polarization of light
The
phenomena of diffraction, bending of light around the corners of a tiny object, Interference, and Polarization of light can only be explained if the light is considered to have a
wave nature. The particle theory of light cannot explain these phenomena.
On the other
hand, the phenomena of refraction and reflection of light and casting of the Shadow
of the object by light can be explained only if the light is thought to be made of
particles.
Physics
experiments over the past hundreds of years or so have demonstrated that light has a dual nature of
light exhibiting the properties of both wave and particle, depending on the situation it is in. The modern
theory of light, called the Quantum theory of
light, combines both wave and particle models of light.















Comments
Post a Comment
please do not enter any spam link in the comment box