LIGHT, Class X Physics MCQ, MCQ Part - 5
MCQ'S
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction with Answers.
Students can solve NCERT Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction Latest Exam Pattern 2023 - 24 Multiple Choice Questions to know their preparation level.
Q1. Examine the above figure and state which of the following options is correct? (One small box in the figure is equal to 1 cm).
(a) The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1.
(b) The mirror has a focal length of -6 cm and will produce
an image of magnification+1.
(c) The mirror has a focal length of -6 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1.
(d) The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce
an image of magnification+1.
Q2. When the object is placed at the centre of curvature, the image is
formed at the centre of curvature, i.e. m
= − 1. A student obtains a blurred
image of a distant object on a screen using a convex lens. To obtain a distinct
image on the screen, he should move the lens:
(a)
Towards the screen.
(b) Away from the screen.
(c) Either towards
or away from the screen
depending upon the position of the object.
(d) To a position very far away from the screen.
Q3. The angle of incidence from air to glass at point O on the hemispherical glass slab is:
(a) 00.
(b) 450.
(d) 900
Q4. Calculate the current flowing through the 10Ω resistor in the following circuit.
(a) 0.6 A.
Q5. When a 4 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor R there is a current of 100 mA in the circuit as shown in the figure. The value of the resistance of the resistor is:
(a) 40 Ω
Q6. The image shows Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Which option explains the rule to understand the working of a motor?
(a)
When a conductor is moved inside a magnetic field, current is
produced in the conductor.
(b)
When a current-carrying conductor is moved with a force, it creates a magnetic field.
(c)
When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic
field, it experiences a force by the magnetic field.
(d)
When a magnetic field is moved relative to the conductor, current is produced
in the conductor.
Q7. In an attempt to demonstrate electrical conductivity through an electrolyte, the following apparatus (Figure) was set up.
Which among the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) The bulb will not glow because the electrolyte is not acidic.
(ii) The bulb will glow because NaOH is a strong base and furnishes
ions for conduction.
(iii) The bulb will not glow because the circuit is incomplete.
(iv)
Bulb will not glow because
it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution.
(a)
(ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c)
(iv) only
(d)
(ii) only
Q8. A student determines the focal length of a device X, by focusing the image of a far-off object on the screen positioned as shown in Figure The device X is a,
(a)
Convex lens
(b)
Concave lens
(c)
Convex mirror
(d)
Concave mirror
Q9. A student traces the path of a ray of light through a
glass prism for different angles of incidence. He analyses each diagram and
draws the following conclusion:
I. On entering the prism, the light ray bends towards its base.
II.
Light ray suffers refraction at the point of incidence and point of emergence
while passing through the prism.
III. An emergent ray bends at a certain angle to the direction
of the incident ray.
IV. While emerging from the prism, the light ray bends
towards the vertex of the prism.
Out of the above inferences, the correct ones are:
(a) I, II, and III
(b) I, III, and IV
(c) II, III and IV
(d) I and IV
Q10. When white light passes through the achromatic combination of prisms,
then what is observed?
(a) Deviation
(b) Dispersion
(c)
Both deviation and dispersion
(d)
Atmospheric refraction
Q11. The following figures
show the path of light
rays through three
lenses marked L1, L2, and L3 and their focal
points F1,
F2, and F3 respectively.
(a)
L1
(b)

L2
(c)
L3
Which of the following diagrams
shows the concave
lens properties?
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Q12. Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?

(a)
Dispersion of light.
(b)
Scattering of light.
(c)
Total internal reflection of light.
(d)
Reflection of light from the earth.
Q13. As light travels from a rarer to a denser medium it will have,
(a)
Increased velocity.
(b)
Decreased velocity.
(c)
Decreased wavelength.
(d)
Both (b) and (c).
Q14. Refraction of light
occurs because of a change in velocity or speed of light in different media.
When a ray of light travels
from a rarer to a denser medium,
it moves towards
the normal. When it travels
from a denser to a rarer medium,
it moves away from the normal. When a light ray travels from a rarer to a denser medium.
its velocity and wavelength both decrease. Which of the following statements
is/are correct for litmus?
1. Litmus solution is a purple dye.
2. It is extracted from lichen.
3. In neutral solution. it remains colourless.
(a) 1 and 2.
(b) 2 and 3.
(c) 1 and 3.
(d) 1, 2 and 3.
Q15.
Dispersion of light by glass prism is shown in the above figure. Here x and y indicates ___________and__________
colour
respectively.
(b) Red, indigo.
(c) Red, yellow.
(d) Violet, green.
(a) Red, blue.
Q16. At the time of the short circuit, the electric current in the circuit:
(a) Vary continuously.
(b) Does not change.
(c) Reduces substantially.
(d) increases heavily.
Q17. A student carries out an experiment and plots the V -I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively (Figure). Which of the following is true?
(a) R1 = R2 = R3
(b) R1 ≥ R2 ≥ R3
(c) R3 ≥ R2 ≥ R1
(d) R2 ≥ R3
≥ R1
Q18. If the key in the arrangement is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are,
(a) concentric circles.
(b) elliptical in shape.
(c) straight lines parallel to each other.
(d) concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it.
Q19. Which of the following statements
is not correct about the magnetic
field?
(a) Magnetic field lines form a continuous closed curve.
(b) Magnetic field lines do not interest
each other.
(c) The direction of a tangent at any point on the magnetic field line curve gives the direction
of a magnetic field at that point.
(d) Outside the magnet, magnetic
field lines go from the South to the North pole of the magnet.
Q20. Which of the following correctly represents the graphical relation between the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of reflection (r)?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Q21. The twinkling of
stars is due to atmospheric,
(a) dispersion of light by water droplets.
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices.
(c) scattering of light by dust particles.
(d) internal reflection of light by clouds.
Q22. An object is immersed in a fluid. So that the object becomes
invisible, it should
(a)
Behave as a perfect reflector.
(b)
Absorb all light falling on it.
(c)
Have a refractive index of one.
(d)
Have a refractive index exactly matching, with that of the surrounding fluid.
Q23. Study the following ray diagram:
In this diagram, the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation respectively have been represented by
(a) y,
p, z
(b) x,
q, z
(c) p,
y, z
(d) p,
z, y
Q24. In the given figure, a light ray AB is incident normally on one face PQ of an equilateral glass prism. The angles at faces PR is:
(a) 600
Q25. Two thin lenses of power + 3.5 D and -2.5 D are placed in contact. The power of the lens combination is-
(a) +1 D
(b) +1.5 D
(c) +2.5 D
(d) +2 D
Q26. A ray of light is refracted as per the following diagram. Which of the following medium is optically denser?
(a) Medium A.
(b) Medium B.
(c) Cannot be identified.
(d) Both mediums are denser.
Q27. Which of the following
phenomena of light are involved
in the formation of a rainbow?
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion.
(b) Reflection, dispersion and total internal
reflection.
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection.
(d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal
reflection.
Q28. The proper representation of a series combination of cells (Figure) obtaining maximum potential is,
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
Q29. Which of the following factors affect the strength of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor
in a uniform magnetic field?
(a) magnetic field
strength
(b) magnitude of current in a conductor
(c) length of the conductor within the magnetic field
(d) All of the above.
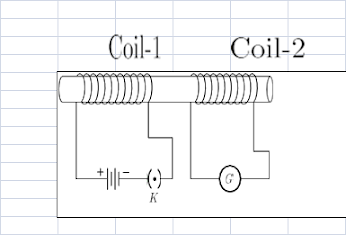
Q30. In the arrangement shown in Figure, there are two coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod. Initially, the key is not inserted. Then the key is inserted and later removed. Then
(a) the
deflection in the galvanometer
remains zero throughout.
(b)
there is a momentary deflection
in the galvanometer but it dies out shortly and there is no effect when the key is removed.
(c)
there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in the same direction.
(d)
there are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in opposite
directions.
Q31.
Commercial electric
motors do not use
(a) an electromagnet to rotate the armature.
(b) effectively a large
number of turns
of conducting wire in the current carrying
coil.
(c) a permanent magnet to rotate
the armature.
(d) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound.
Q32.
A cylindrical conductor of length
l
and uniform area of cross-section A has resistance R. Another conductor of length 21 and resistance R of the same material has an area of cross-section
(b) 3A/2
(c) 2 A
(d) 3 A
(a) A/2
Q33.
A



































Comments
Post a Comment
please do not enter any spam link in the comment box